Introduction to Data Centers
Data center networking is essential to the modern corporate environment; they are sometimes called the unsung heroes of the digital age. These centralized locations, which house a variety of vital components like servers, storage devices, and networking hardware, act as the hubs of the information technology industry. In a sense, they serve as the digital fortifications that store and handle the heartbeats of numerous companies, guaranteeing the smooth flow of data that drives our interconnected world.
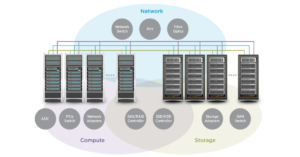
Importance of Data Center Networking
Networking is the common thread that connects all the different parts of the enormous data center ecosystem. The unseen force that makes it possible for servers, storage devices, and networking hardware to connect its data center networking, in particular. It is the foundation for a data center’s operations, allowing data to move freely and effectively between locations. This component is crucial since it directly affects the overall data center infrastructure’s performance and dependability.
Components of a Data Center
A typical data center is an intricate combination of several parts that cooperate to provide end customers with data and services. It consists of several strong servers that run applications and handle data. These servers are supported by networking hardware, such as switches, routers, and security appliances, which enable the smooth transfer of data and storage arrays, which house enormous amounts of data.
Types of Data Center Networks
Data center networks are available in various sizes and shapes, each tailored to satisfy particular demands. Let’s examine the different kinds:
Local Area Network (LAN)
The backbone of internal data center operations is LANs. They link gadgets inside a limited geographic space, such as a campus or a single building. LANs are essential for quickly transferring data between servers, storage devices, and other resources since they are made for high-speed data transmission.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
Conversely, WANs connect several LANs over larger geographic distances—typically spanning cities, regions, or even entire nations. They are essential for establishing connections between various data centers and distant offices, making resource sharing and smooth communication possible.
Storage Area Network (SAN)
Data centers use specialized networks called SANs for data retrieval and storage. These technical networks guarantee the effective administration of enormous amounts of data by offering high-speed access to storage devices. The foundation of data centers’ data storage, SANs maximize dependability and performance.
Data Center Topologies
A data center’s network topology design is important since it directly affects scalability and dependability. There are three frequently used common topologies:
Bus Topology
Every device in a bus topology is linked to a single central cable. This architecture can be less dependable even though it is simple and affordable because it is susceptible to a single cable failure that could take down the entire network.
Star Topology
In contrast, star topology links every device to a single hub or switch. Compared to the bus topology, this approach offers improved dependability and easier troubleshooting. Network integrity is maintained since a single device failure affects only that one device.
Ring Topology
Ring topology entails creating closed-loop connections between devices. It resists cable failures, but managing and maintaining it cannot be easy. This architecture lowers latency and promotes effective data transfer by guaranteeing data flow in both directions.
Network Protocols in Data Centers
Several fundamental protocols are needed for data center networking to guarantee efficient data transfer and communication. These are a few of the basic protocols:
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol)
The foundation of contemporary networking is TCP/IP, which controls data transmission across networks, including data centers. The internet is supported by this strong, dependable protocol, which allows data to travel great distances while retaining integrity.
Ethernet
The common LAN technology known as Ethernet specifies the structure and method of data packet transmission via local area networks. It offers a uniform foundation so that devices on a LAN can interact with each other efficiently.
Fiber Channel
Fiber Channel is the preferred high-speed networking technology in storage area networks (SANs) for establishing connections between storage devices. It provides the high throughput and low latency required for efficiently maintaining and retrieving large volumes of data.
Virtualization in Data Centers
Data center operations have been completely transformed by the revolutionary technology known as virtualization. By enabling the operation of numerous virtual servers on a single physical server, it maximizes data center flexibility and resource utilization. The data center infrastructure’s adaptability has risen, and hardware costs have dropped dramatically because of this innovation.
Security Measures in Data Center Networking
Data centers must be extremely secure since they play a vital role in protecting sensitive data. The following are some crucial security precautions:
Firewalls
Data centers’ first line of defense is their firewalls, which filter incoming and outgoing network traffic. They protect data and infrastructure by enforcing stringent security measures that stop unwanted access and cyberattacks.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
IDS monitors network traffic to look for unusual or suspicious patterns or activity. IDS notifies administrators of anomalous activity, enabling them to look into and quickly address possible security breaches.
Data Encryption
Data encryption, a fundamental security technique, transforms sensitive information into unintelligible code. This guarantees data privacy even if it ends up in the wrong hands. When it comes to protecting data both during transmission and storage, encryption is essential.
Scalability and Redundancy
Because data centers are made to be scalable, companies may add more infrastructure as their demands develop. Data centers that are scalable can handle growing workloads, ensuring their future-proofness. Redundancy measures are also used to ensure uninterrupted operation during hardware breakdowns. To reduce downtime and preserve reliability, redundancy in components and failover solutions are important.
Monitoring and Management
To maintain peak performance and spot problems, data center managers need to have access to efficient monitoring and management tools. Real-time monitoring makes proactive troubleshooting and resource allocation possible, which guarantees the data center’s safe and effective operation.
Cloud Integration
To improve their capabilities, many contemporary data centers interact with cloud services. Because of this integration, businesses may use cloud-based services and expand resources dynamically, which increases flexibility and reduces costs. The ability of hybrid cloud solutions to integrate cloud infrastructure with on-premises data centers has made them increasingly desirable.
Future Trends in Data Center Networking
Keeping an eye on new trends and technologies is essential to staying ahead of the data center networking curve. Two key themes will impact data centers in the future:
Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
By separating the control plane from the data plane, SDN completely changes networking in data centers. This makes network resource management more programmable and flexible. Modern data centers require SDN because it makes network management easier, automates processes, and increases agility.
Edge Computing
The need for low-latency services and applications is driving the rise of edge computing. Real-time application performance is enhanced, and latency is decreased via edge data centers situated closer to end users. They are especially important for applications requiring split-second decision-making, such as augmented reality, IoT, and driverless cars.
Conclusion
In summary, data center networking is the unsung hero of the digital age because it forms the foundation of contemporary companies and organizations. Anyone stepping into the world of information technology must have a thorough understanding of its complex components, varied topologies, and strong security mechanisms. By demystifying data center networking, you will have a better understanding of and appreciation for this essential component of the digital era, opening the door for more developments in the ever-changing field of information technology.

